In today’s fast-paced world of logistics, manufacturing, and retail, the choice of label materials can significantly impact business efficiency and overall product success. A simple label might not seem important, but when you consider the implications of faded barcodes, peeling stickers, or illegible product details, the material choice suddenly takes on new weight. From improving brand appeal to maintaining strict regulatory compliance, picking the right label material is crucial. This guide will help you navigate the complex world of label materials, so you can make an informed choice that benefits your operations and bottom line.
1. The Crucial Role of Label Materials
When it comes to labels, one size does not fit all. The material must be chosen based on the environment it will be exposed to, the lifespan required, and the cost constraints. Here’s why the right material matters:
Longevity and Durability
Imagine a barcode on a product in a warehouse that fades over time. Scanners won’t read it, leading to inventory management issues. Or consider a shipping label that smudges in the rain, causing delivery delays. Labels need to be able to withstand specific conditions, from exposure to moisture and heat to abrasions in high-friction environments. Choosing a material that holds up to these challenges can save businesses from costly mishaps.
Cost-Effectiveness
Sometimes, it’s tempting to choose the cheapest label material to cut costs. However, when labels fail, the cost of replacements and the potential for operational inefficiencies can outweigh the initial savings. It’s about striking a balance between upfront expenses and long-term durability.
Industry Compliance
In some sectors, using the wrong type of label isn’t just inefficient—it could also be illegal. The healthcare industry, for example, requires labels that adhere to strict standards for patient safety, while the chemical industry must follow specific guidelines to ensure safe handling and hazard communication.
2. Exploring the Variety of Label Materials
Label materials come in a wide range, each with unique properties. Here’s a deep dive into the different types:
2.1 Direct Thermal Labels
Direct thermal labels use heat-sensitive materials that darken when exposed to a thermal printhead. They’re a popular choice for applications that require a short lifespan.
- Characteristics: Direct thermal labels are known for their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. They require no ink or ribbon, making the printing process efficient.
- Applications: Common uses include shipping labels, event tickets, and temporary tags. Businesses that need labels for short-term use or environments where quick readability is essential often opt for direct thermal labels.
- Limitations: These labels are prone to fading, especially when exposed to sunlight or high heat. They are not recommended for long-term applications or those requiring durable, archival-grade labeling.
Example: Picture a scenario in a bustling warehouse. Direct thermal labels are used to tag packages for delivery. They’re clear, easily scannable, and sufficient for the job—but only for a few weeks. Beyond that, they start to lose clarity, making them unsuitable for long-term storage or outdoor use.
2.2 ArtPaper Labels
ArtPaper labels are high-quality coated paper labels designed to produce vibrant and eye-catching prints. They’re perfect for applications where presentation matters.
- Material Composition: The coating provides a smooth, glossy finish that enhances color printing. This makes ArtPaper labels a favorite for product packaging and marketing purposes.
- Benefits: Excellent print clarity and cost-effectiveness. They’re suitable for indoor use and can withstand temperatures between 20°C and 80°C.
- Drawbacks: ArtPaper labels are not suitable for moisture-prone or harsh environments. They’re less durable than polyester or synthetic options.
Applications: Pharmaceutical labels, food packaging, and premium brand labels are often printed on ArtPaper for that polished, high-end look.
2.3 Polyester Labels
For maximum durability, polyester labels are the go-to choice. These labels are made from a synthetic material that resists water, chemicals, and abrasion.
- Strength and Versatility: Polyester labels are suitable for outdoor use and environments where labels are exposed to harsh elements. They can withstand temperatures ranging from -40°C to 150°C, making them ideal for extreme conditions.
- Industrial Applications: These labels are often used for asset tracking in industrial settings, equipment labeling, and compliance marking for hazardous materials.
- Pros and Cons: While they are more expensive than paper-based labels, the investment pays off for long-term use. The only downside is the higher upfront cost, which can be a hurdle for businesses on a tight budget.
Example: Consider an oil and gas facility where equipment is exposed to harsh weather conditions. Polyester labels are essential for tagging assets and ensuring data remains intact, even in the toughest environments.
2.4 Inkjet Labels
Inkjet labels are designed for high-resolution, photo-quality printing. They work best with inkjet printers and are used for applications requiring vibrant and detailed images.
- Material Options: Inkjet labels can be made from paper or synthetic materials, depending on the desired durability. They are perfect for printing marketing materials, product labels, and custom graphics.
- Print Quality: The main advantage of inkjet labels is their superior print quality. Images come out crisp and colors vibrant, ideal for branding and promotional materials.
- Challenges: The downside is that inkjet labels may require protective coatings to prevent smudging or fading, especially in high-moisture environments.
Use Case: Small businesses often use inkjet labels for custom product packaging, like artisanal food jars or handcrafted beauty products, where a professional look is essential.
3. Comparison Guide
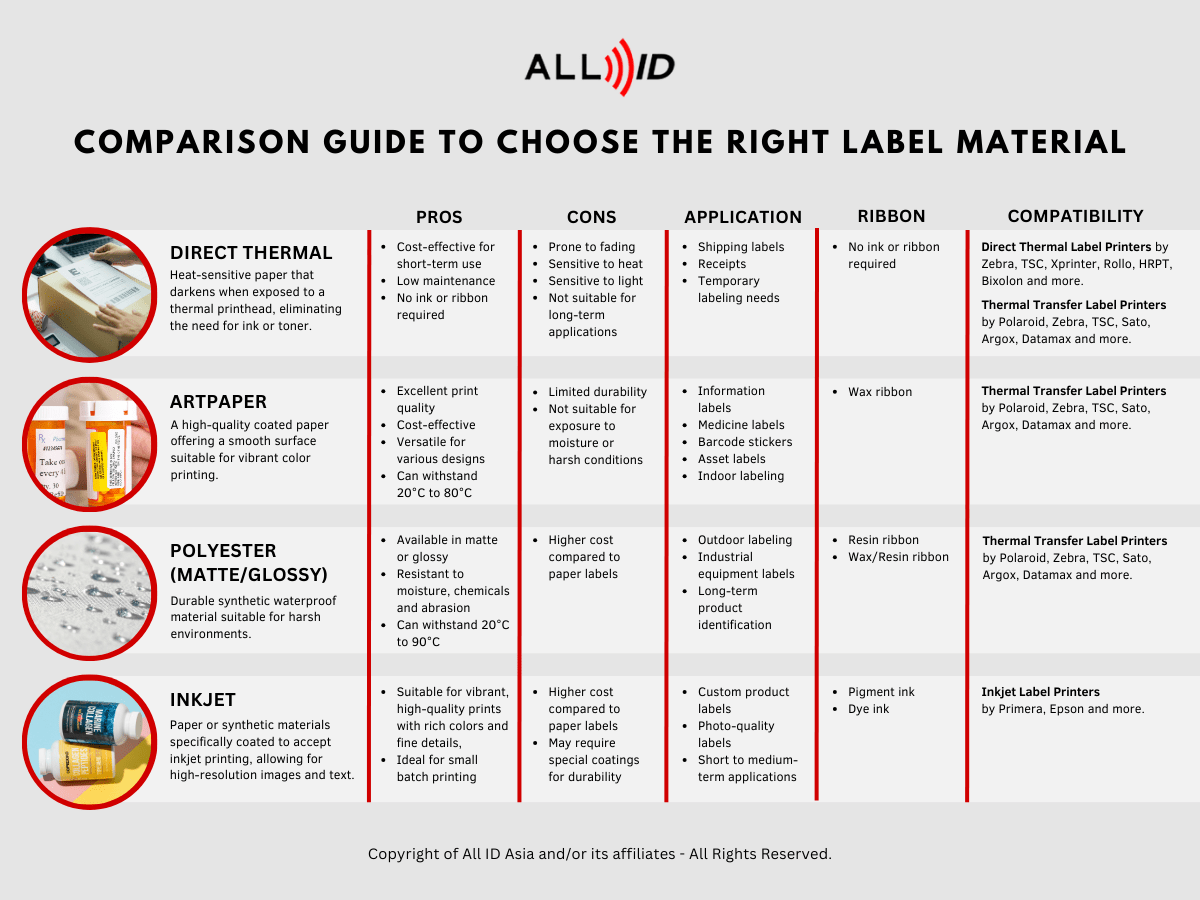
The comparison guide above offers a visual representation of the differences between various label materials. It’s a helpful tool for quickly understanding which material might suit your needs. Let’s summarize some of the key points:
- Direct Thermal: Best for temporary labeling needs.
- ArtPaper: Great for vibrant, high-quality prints but not moisture-resistant.
- Polyester: Highly durable and suited for harsh environments.
- Inkjet: Offers high-resolution prints for custom and short-run applications.
Understanding these distinctions can help you make an informed decision and optimize your label printing process.
4. Advanced Label Printing Technologies
Label printing has evolved significantly over the years, with new technologies enhancing speed, precision, and efficiency. Here’s a look at some advanced options:
4.1 Thermal Transfer Printing
Thermal transfer printing uses a heated ribbon to create durable images on labels. It’s ideal for applications requiring long-lasting, high-quality prints.
- Process Overview: The heated ribbon melts ink onto the label material, creating an image that resists fading and abrasion.
- Applications: Widely used in industrial labeling, such as for chemical containers, automotive parts, and outdoor equipment.
- Benefits: Superior print durability compared to direct thermal printing.
4.2 Laser Printing Technologies
Laser printing is known for its speed and precision. It uses laser beams to etch images onto the label surface, making it a non-contact method that minimizes material wear and tear.
- How It Works: The laser beam activates the label material’s surface, ensuring high-definition prints.
- Ideal Uses: Electrical component labeling, signage, and applications where fine details are crucial.
- Pros and Cons: While efficient and precise, laser printing equipment is often more expensive, making it a better fit for large-scale operations.
4.3 RFID-Enabled Labels
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) labels incorporate microchips that communicate data wirelessly. They’re used for advanced inventory management and real-time asset tracking.
- Technology Breakdown: RFID labels contain a microchip and antenna embedded in the label material. This setup allows data to be read without direct line-of-sight.
- Logistics Benefits: Perfect for large warehouses, retail inventory management, and automated checkout systems.
- Challenges: Higher costs and the need for specialized equipment can be a barrier for smaller businesses.
5. Factors to Consider When Choosing Label Materials
Selecting the right label material isn’t just about cost or appearance. Here are some factors to weigh:
5.1 Environmental Conditions
- Temperature Resistance: If labels will be exposed to extreme heat or cold, choose a material that won’t degrade. Polyester and certain synthetics perform well in these environments.
- Moisture and Humidity: Water-resistant labels, like polyester, are necessary for outdoor or high-humidity areas.
5.2 Adhesive Types
- Permanent Adhesives: Best for labels that need to stay put, even in harsh conditions.
- Removable Adhesives: Ideal for temporary labels that won’t leave residue when removed.
- Specialty Adhesives: There are options designed for low-surface-energy plastics, oily surfaces, or extreme heat.
5.3 Cost-Benefit Analysis
Balancing cost with performance is essential. Consider the long-term savings of using durable materials versus the short-term gains of cheaper labels.
Example: A company shipping perishable goods may benefit more from investing in moisture-resistant labels to ensure scannability, even if it means a higher initial cost.
6. Label Printing for Compliance and Safety
Compliance isn’t just a buzzword; it’s a necessity in many industries. Regulatory bodies often dictate the type of label material and adhesive required.
6.1 Pharmaceutical Industry
- Tamper-Evident Labels: These labels ensure that products haven’t been tampered with, protecting consumer safety.
- Sterile and Durable: Labels must be able to withstand sterilization processes and remain legible for the product’s life span.
6.2 Food and Beverage Industry
- FDA Regulations: Labels must be made from materials safe for food contact. Discuss food-safe adhesives and the importance of avoiding contamination.
- Traceability: Labels should include batch numbers and expiry dates for product recalls.
6.3 Chemical Labeling and GHS Compliance
- Hazard Labels: Chemical containers must be labeled in compliance with OSHA’s GHS (Globally Harmonized System) standards. Discuss the importance of durability and chemical resistance.
7. Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Understanding how label materials solve real-world problems can provide valuable insight. Here are some examples:
7.1 Retail Brand Success Story
- The Challenge: A retail brand needed labels that would make their seasonal products stand out on shelves while being cost-effective.
- The Solution: ArtPaper labels were chosen for their vibrant colors and print clarity, leading to increased sales and improved brand recognition.
7.2 Industrial Manufacturer’s Dilemma
- The Problem: An industrial manufacturer struggled with equipment labels degrading outdoors.
- The Fix: Switching to polyester labels solved the problem, improving operational efficiency and reducing label replacement costs.
Lesson Learned: Using the right label material not only solves problems but can also create a better experience for end users.
8. The Future of Label Printing
As technology and environmental concerns evolve, so do label materials. Here’s what the future holds:
8.1 Sustainability Trends
- Eco-Friendly Labels: More companies are opting for biodegradable or recyclable labels. Discuss the impact on waste reduction and brand image.
- Recycling Initiatives: How companies are implementing closed-loop recycling systems to minimize label waste.
8.2 Smart Labels and the Internet of Things (IoT)
- How They Work: Smart labels can interact with smartphones or other devices, providing information about the product’s freshness, location, or authenticity.
- Applications: Use cases range from food safety monitoring to inventory control in large warehouses.
Selecting the right label material involves understanding your specific needs, industry requirements, and budget. Whether you’re printing labels for a warehouse, a retail store, or a medical facility, there’s a material designed to optimize efficiency and ensure durability.
Ready to streamline your labeling process and choose the best material for your needs? Visit barcode.com.sg and explore our range of high-quality label materials and advanced printing solutions!



























